|
RKH
|
|
RKH
|
Describes a submachine state. More...
#include <rkhsm.h>
Data Fields | |
| RKHROM RKH_TR_T * | trtbl |
| Points to state transition table. | |
| RKHROM RKH_EXPCN_T * | exptbl |
| Points to state transition table. | |
| RKHROM RKH_RSM_T * | sbm |
| Points to submachine object. | |
Describes a submachine state.
A submachine state is a kind of a state that actually refers to another defined state machine. A submachine state is logically equivalent to the insertion of the referenced state machine as a composite state in the place of the submachine state. Consequently, every entrance to a submachine state is equivalent to the corresponding entrance to the inserted (referenced) composite state. In particular, it can be entered thruough its initial pseudostate (as any other composite state), or through one of its entry points.
Similary, every exit from a submachine state is equivalent to the corresponding exit from the inserted composite state. It can be exited through one of its exit points. When it is exited through its exit point the effect of the transition targeting the exit point is executed first, followed by the exit behavior of the composite state.
The entry, exit, and behavior actions and internal transitions are defined as part of the state. Submachine state is a decomposition mechanism that allows factoring of common behaviors and their reuse.
The purpose od defining submachine states is to decompose and localize repetitive parts because the same state machine can be referenced from more than one submachine state.
The diagram in following figure shows a fragment from a state machine diagram in which a submachine state (the SB) is referenced.
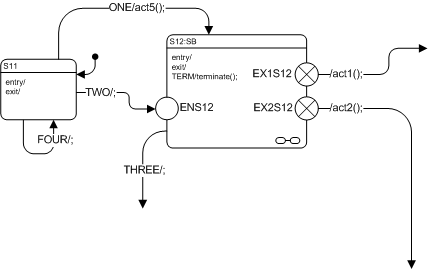
In the above example, the transition triggered by event TWO will terminate on entry point ENS12 of the SB state machine. The ONE transition implies taking of the default transition of the SB and executes the act5() action. The transition emanating from the EX1S12 exit point of the submachine will execute the act1() behavior in addition to what is executed within the SB state machine. Idem transition emanating from the EX2S12. This transition must have been triggered within the SB state machine. Finally, the transition emanating from the edge of the submachine state is triggered by event THREE.
The following figure is an example of a state machine SB defined with two exit points, EXPNT1 and EXPNT2, and one entry point ENPNT.

point"
In the following figure the state machine shown above is referenced twice in a submachine state S12 and S2.